Excel VBA ENVIRON (entorno)
La función VBA ENVIRON (significa ENVIRONMENT ) que se puede clasificar como una función de información, ya que esta función devuelve los valores para las variables de entorno de un sistema operativo. Las variables de entorno (sistema operativo) contienen información sobre los perfiles de todos los usuarios, nombre de usuario, perfil de usuario, una carpeta de inicio para el usuario, etc. Esta función devuelve un valor de cadena.
Sintaxis

Esta función tiene solo un argumento que es ' Expresión'. Podemos especificar la posición numérica (valor entero) que representa la posición numérica de la variable de entorno en la tabla de variables de entorno o el nombre de la variable en sí.
Si especificamos la posición numérica, la función devuelve la variable de entorno y su valor, ambos con un signo igual en el medio.

Si especificamos el nombre de la variable, la función devuelve el único valor.

Salida:
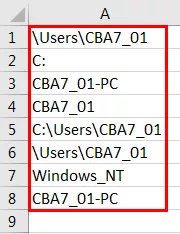
¿Cómo usar la función Environ en VBA?
Ejemplo 1
Abra el símbolo del sistema usando la función ENVIRON en VBA .
Para hacer lo mismo, los pasos serían:
Inserte el botón de comando usando el comando 'Insertar' disponible en el grupo 'Controles' en la pestaña 'Desarrollador' o use la tecla de acceso directo de Excel ( Alt + F11 ).

Si la pestaña 'Desarrollador' no está visible, siga los siguientes pasos para hacerla visible.
Haga clic en 'Archivo' y elija 'Opciones' de la lista.

Elija 'Personalizar cinta' en el menú de la izquierda y marque la casilla de la pestaña 'Desarrollador' y haga clic en 'Aceptar'.
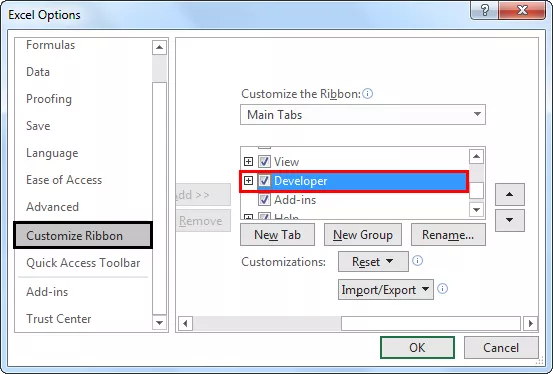
Ahora la 'pestaña Desarrollador' está visible.
Mientras insertamos el botón de comando, si seguimos presionando la tecla ALT , los bordes del botón de comando estarán junto con el borde de la celda. Cambie las propiedades del botón de comando insertado usando el menú contextual, que obtenemos haciendo clic derecho en el 'Botón de comando'.

Ventana Propiedades

Para escribir el código VBA para el botón de comando, debemos seleccionar el botón de comando y elegir 'Ver código' en el menú contextual.

Escriba el código de la siguiente manera:

Hemos llamado a la función 'Shell' para escribir comando para ejecutar un programa (en nuestro caso, símbolo del sistema).
Hemos utilizado 'ComSpec', que significa 'Especificador de comando'.
Ahora salga de VBE y haga clic en el botón de comando. Hemos mostrado un símbolo del sistema.
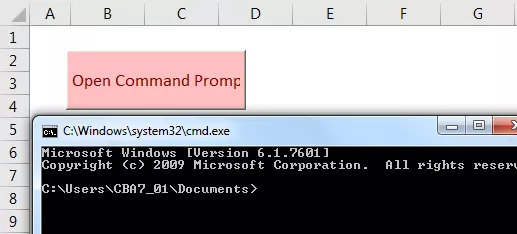
Ejemplo # 2
Supongamos que queremos extraer los nombres de archivo y los detalles de la carpeta seleccionada de la siguiente manera.
Los pasos para hacer lo mismo son:
Rellena las celdas B2: H9 con color naranja claro.

Cree la etiqueta usando el comando 'Insertar' en el grupo 'Controles' en el 'Desarrollador'.

Cree las etiquetas que se muestran a continuación y edite las propiedades como título , BackColor , BackStyle , BorderStyle , Shadow.
Cree el cuadro combinado de la siguiente manera utilizando el comando Cuadro combinado (uno de los controles ActiveX) disponible en el comando Insertar en el grupo Controles del desarrollador.
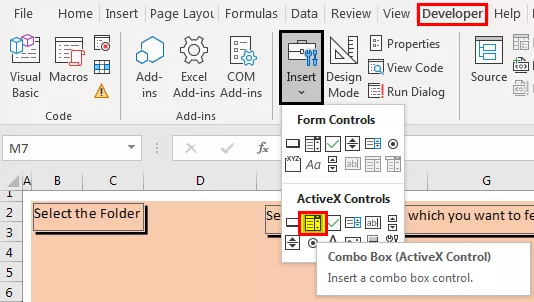
Después de crear el cuadro combinado en Excel de la siguiente manera, podemos cambiar las propiedades.

We will add code for the list to be displayed in the combo box using the View Code command in the contextual menu.

It is a code for “Select the Folder” ComboBox.
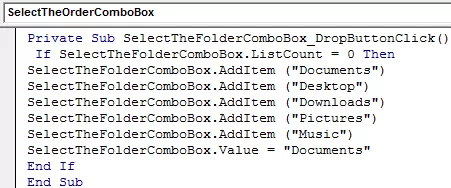
It is a code for “SortBy” ComboBox.

It is a code for “Select the Order” ComboBox.

We will create a list box containing all file types to select them to get only that types of files in the result. To do the same, please choose “List Box (ActiveX Control)” from the “Insert” command in the “Controls” group in the “Developer” tab.

Drag the list box, as shown below.

Change the properties of the list box as follows.

To add the file types to the list box, please use the following code.
Write the code in “This workbook.”
Code:
Private Sub Workbook_Open() Dim ArrFileType(25) As Variant ArrFileType(0) = "Microsoft Excel 97-2003 Worksheet(.xls)" ArrFileType(1) = "Microsoft Office Excel Worksheet(.xlsx)" ArrFileType(2) = "Microsoft Excel Macro-Enabled Worksheet(.xlsm)" ArrFileType(3) = "Word Document 97-2003(.doc)" ArrFileType(4) = "Word Document 2007-2010(.docx)" ArrFileType(5) = "Text Document(.txt)" ArrFileType(6) = "Adobe Acrobat Document(.pdf)" ArrFileType(7) = "Compressed (zipped) Folder(.Zip)" ArrFileType(8) = "WinRAR archive(.rar)" ArrFileType(9) = "Configuration settings(.ini)" ArrFileType(10) = "GIF File(.gif)" ArrFileType(11) = "PNG File(.png.webp)" ArrFileType(12) = "JPG.webp File(.jpg.webp)" ArrFileType(13) = "MP3 Format Sound(.mp3)" ArrFileType(14) = "M3U File(.m3u)" ArrFileType(15) = "Rich Text Format(.rtf)" ArrFileType(16) = "MP4 Video(.mp4)" ArrFileType(17) = "Video Clip(.avi)" ArrFileType(18) = "Windows Media Player(.mkv)" ArrFileType(19) = "SRT File(.srt)" ArrFileType(20) = "PHP File(.php)" ArrFileType(21) = "Firefox HTML Document(.htm, .html)" ArrFileType(22) = "Cascading Style Sheet Document(.css)" ArrFileType(23) = "JScript Script File(.js)" ArrFileType(24) = "XML Document(.xml)" ArrFileType(25) = "Windows Batch File(.bat)" Sheet2.FileTypesListBox.List = ArrFileType End Sub
Insert the checkboxes using the same “Insert” command in the “Controls” group in the “Developer” tab and change the properties for inserted ‘Checkboxes’ using the ‘Properties’ power available in the same group after selecting the objects.

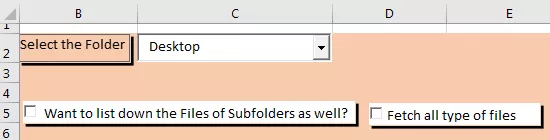
Insert command buttons using the ‘Insert’ command available in the same group and change the properties like a caption and other stuff.

We have formed the entire structure. Now we need to write the code.
Activate the ‘Design Mode,’ and right-click on the “Fetch all files details” button to choose the “View Code” from the contextual menu to add the code for the switch.
We will declare some variables first in the module.
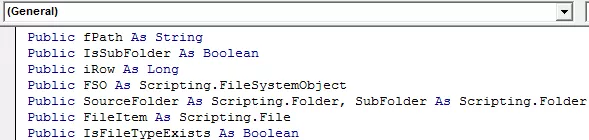
Below is the code added to a “Fetch all files details” button.
Code:
Private Sub FetchFilesBtnCommandButton_Click() iRow = 14 fPath = Environ("HOMEPATH") & " " & SelectTheFolderComboBox.Value If fPath "" Then Set FSO = New Scripting.FileSystemObject If FSO.FolderExists(fPath) False Then Set SourceFolder = FSO.GetFolder(fPath) If Sheet2.IncludingSubFoldersCheckBox.Value = True Then IsSubFolder = True Else IsSubFolder = False If SourceFolder.Files.Count = 0 Then MsgBox "No files exists in this Folder" & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & "Check your folder path and Try Again !!", vbInformation Exit Sub End If End If Call ClearResult If FetchAllTypesOfFilesCheckBox.Value = True Then Call ListFilesInFolder(SourceFolder, IsSubFolder) Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "C14", "D14", "E14") Else Call ListFilesInFolderXtn(SourceFolder, IsSubFolder) Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "C14", "D14", "E14") End If FilesCountLabel.Caption = iRow - 14 Else MsgBox "Selected Path Does Not Exist !!" & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & "Select Correct One and Try Again !!", vbInformation End If Else MsgBox "Folder Path Can not be Empty !!" & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & "", vbInformation End If End Sub
Define the ‘ClearResult’ function in the module. To insert the module, select ‘ThisWorkbook’ then ‘Insert’ and then ‘Module”’.
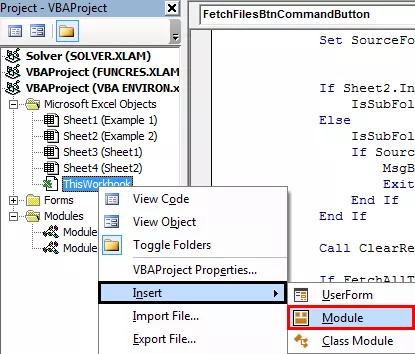
Write the following code in the module.
Code for ClearResult
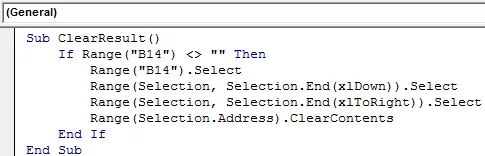
There are more subroutines like ‘ListFilesInFolder,’ ‘ListFilesInFolderXtn,’ ‘ResultSorting,’ we will define all these subroutines in the module.
‘ListFilesInFolder’
Code:
Public Sub ListFilesInFolder(SourceFolder As Scripting.Folder, IncludeSubfolders As Boolean) On Error Resume Next For Each FileItem In SourceFolder.Files ' display file properties Cells(iRow, 2).Formula = iRow - 13 Cells(iRow, 3).Formula = FileItem.Name Cells(iRow, 4).Formula = FileItem.Path Cells(iRow, 5).Formula = Int(FileItem.Size / 1024) Cells(iRow, 6).Formula = FileItem.Type Cells(iRow, 7).Formula = FileItem.DateLastModified Cells(iRow, 8).Select Selection.Hyperlinks.Add Anchor:=Selection, Address:= _ FileItem.Path, TextToDisplay:="Click Here to Open" 'Cells(iRow, 8).Formula = "=HYPERLINK(""" & FileItem.Path & """,""" & "Click Here to Open" & """)" iRow = iRow + 1 ' next row number Next FileItem If IncludeSubfolders Then For Each SubFolder In SourceFolder.SubFolders ListFilesInFolder SubFolder, True Next SubFolder End If Set FileItem = Nothing Set SourceFolder = Nothing Set FSO = Nothing End Sub
‘ListFilesInFolderXtn’
Public Sub ListFilesInFolderXtn(SourceFolder As Scripting.Folder, IncludeSubfolders As Boolean) On Error Resume Next Dim FileArray As Variant FileArray = Get_File_Type_Array For Each FileItem In SourceFolder.Files Call ReturnFileType(FileItem.Type, FileArray) If IsFileTypeExists = True Then Cells(iRow, 2).Formula = iRow - 13 Cells(iRow, 3).Formula = FileItem.Name Cells(iRow, 4).Formula = FileItem.Path Cells(iRow, 5).Formula = Int(FileItem.Size / 1024) Cells(iRow, 6).Formula = FileItem.Type Cells(iRow, 7).Formula = FileItem.DateLastModified Cells(iRow, 8).Select Selection.Hyperlinks.Add Anchor:=Selection, Address:= _ FileItem.Path, TextToDisplay:="Click Here to Open" 'Cells(iRow, 8).Formula = "=HYPERLINK(""" & FileItem.Path & """,""" & "Click Here to Open" & """)" iRow = iRow + 1 ' next row number End If Next FileItem If IncludeSubfolders Then For Each SubFolder In SourceFolder.SubFolders ListFilesInFolderXtn SubFolder, True Next SubFolder End If Set FileItem = Nothing Set SourceFolder = Nothing Set FSO = Nothing End Sub
‘ResultSorting’
Sub ResultSorting(xlSortOrder As String, sKey1 As String, sKey2 As String, sKey3 As String) Range("C13").Select Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).Select Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlToRight)).Select Selection.Sort Key1:=Range(sKey1), Order1:=xlSortOrder, Key2:=Range(sKey2 _ ), Order2:=xlAscending, Key3:=Range(sKey3), Order3:=xlSortOrder, Header _ :=xlGuess, OrderCustom:=1, MatchCase:=False, Orientation:=xlTopToBottom _ , DataOption1:=xlSortNormal, DataOption2:=xlSortNormal, DataOption3:= _ xlSortNormal Range("B14").Select End Sub
In ‘ListFilesInFolderXtn’ subroutine, we have called a function named ‘ReturnFileType’ and ‘GetFileTypeArray’, we need to define the functions in the same module.
‘ReturnFileType’
Code:
Public Function ReturnFileType(fileType As String, FileArray As Variant) As Boolean Dim i As Integer IsFileTypeExists = False For i = 1 To UBound(FileArray) + 1 If FileArray(i - 1) = fileType Then IsFileTypeExists = True Exit For Else IsFileTypeExists = False End If Next End Function
‘GetFileTypeArray’
Code:
Public Function Get_File_Type_Array() As Variant Dim i, j, TotalSelected As Integer Dim arrList() As String TotalSelected = 0 For i = 0 To Sheet2.FileTypesListBox.ListCount - 1 If Sheet2.FileTypesListBox.Selected(i) = True Then TotalSelected = TotalSelected + 1 End If Next ReDim arrList(0 To TotalSelected - 1) As String j = 0 i = 0 For i = 0 To Sheet2.FileTypesListBox.ListCount - 1 If Sheet2.FileTypesListBox.Selected(i) = True Then arrList(j) = Left(Sheet2.FileTypesListBox.List(i), InStr(1, Sheet2.FileTypesListBox.List(i), "(") - 1) j = j + 1 End If Next Get_File_Type_Array = arrList End Function
We have a command button captioned as ‘Export to Excel File,’ we need to write the code for this button as follows:


In Module, define the subroutine named ‘Export_to_excel.’
Code:
Sub Export_to_excel() On Error GoTo err Dim xlApp As New Excel.Application Dim xlWB As New Workbook Set xlWB = xlApp.Workbooks.Add 'xlWB.Add xlApp.Visible = False ThisWorkbook.Activate Range("B13").Select Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).Select Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlToRight)).Select Selection.Copy xlApp.Visible = True xlWB.Activate xlWB.Sheets("Sheet1").Select xlWB.Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B2").PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues xlWB.Sheets("Sheet1").Cells.Select xlWB.Sheets("Sheet1").Cells.EntireColumn.AutoFit xlWB.Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B2").Select Exit Sub err: MsgBox ("Error Occured while exporting. Try again") End Sub
We have one more command button captioned as ‘Export to Text File.’ We will write the code for the command button as follows:


In this code, we can see that we have a user form, which we need to design using the following steps:
Right Click on the ‘Sheet2 (Example2)’ sheet and choose ‘Insert’ and then ‘UserForm’ from the menu.

Design the UserForm using tools from the toolbox.
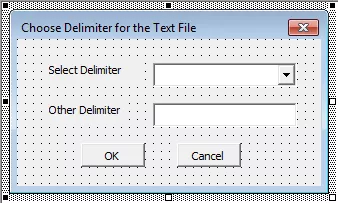
We have used ‘Labels,’ ‘Combo Box,’ ‘Text Box,’ and ‘Command buttons’ for the Userform and have changed caption and name for all the components.
For the first command button (OK), we have to write the code as follows:
Code:
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click() Dim iSeperator As String If ComboBox1.Value = "Other" Then iSeperator = TextBox1.Value Else iSeperator = ComboBox1.Value End If If iSeperator = "" Then If MsgBox("Hello You have not selected any delimeter." & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & _ " It will be very difficult to read the Text file, without specific delimiter", vbYesNo) = vbYes Then Call textfile(iSeperator) Else Exit Sub End If Else Select Case ComboBox1.ListIndex Case 0: iSeperator = "," Case 1: iSeperator = "|" Case 2: iSeperator = "vbTab" Case 3: iSeperator = ";" End Select Call textfile(iSeperator) Unload Me End If End Sub
We have called the ‘textfile’ function in the subroutine for the command button, so we need to define the ‘textfile’ function in the module.
Code:
Sub textfile(iSeperator As String) Dim iRow, iCol Dim iLine, f ThisWorkbook.Activate Range("B13").Select TotalRowNumber = Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).Count - 12 If iSeperator "vbTab" Then Open ThisWorkbook.Path & "File1.txt" For Output As #1 Print #1, "" Close #1 Open ThisWorkbook.Path & "File1.txt" For Append As #1 For iRow = 13 To TotalRowNumber iLine = "" For iCol = 2 To 7 iLine = iLine & iSeperator & Cells(iRow, iCol).Value Next Print #1, iLine Next Close #1 Else Open ThisWorkbook.Path & "File1.txt" For Output As #1 Print #1, "" Close #1 Open ThisWorkbook.Path & "File1.txt" For Append As #1 For iRow = 13 To TotalRowNumber iLine = "" For iCol = 2 To 7 iLine = iLine & vbTab & Cells(iRow, iCol).Value Next Print #1, iLine Next Close #1 End If f = Shell("C:WINDOWSotepad.exe " & ThisWorkbook.Path & "File1.txt", vbMaximizedFocus) MsgBox "Your File is saved in " & ThisWorkbook.Path & "File1.txt" End Sub
For command button 2 (Cancel), we need to write the following code. Double click on the cancel button to write the code.
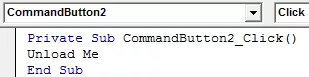
For the Combo Box for selecting a specifier, write the following code.

For the UserForm, write the following code.
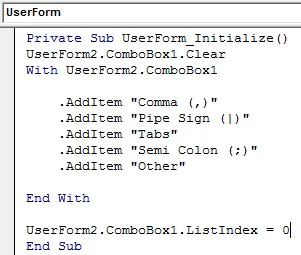
For the ‘Fetch all type of files’ checkbox, write the following code.

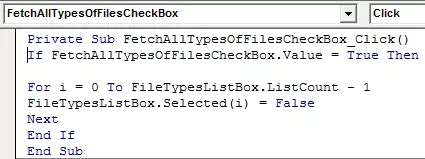
For the ‘ListBox’ for file types, write the following code.


For the ‘SelectTheOrder’ combo box, write the following code.

Code:
Private Sub SelectTheOrderComboBox_Change() Select Case (SelectTheOrderComboBox.Value) Case "Ascending" If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Name" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "C14", "E14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Type" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "F14", "E14", "C14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Size" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "E14", "C14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "Last Modified" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "G14", "C14", "E14") End If Case "Descending" If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Name" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "C14", "E14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Type" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "F14", "E14", "C14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Size" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "E14", "C14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "Last Modified" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "G14", "C14", "E14") End If Case Default Exit Sub End Select End Sub
For the ‘Sort by’ combo box, we will write the following code.

Code:
Private Sub SortByComboBox_Change() Select Case (SelectTheOrderComboBox.Value) Case "Ascending" If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Name" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "C14", "E14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Type" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "F14", "E14", "C14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Size" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "E14", "C14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "Last Modified" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "G14", "C14", "E14") End If Case "Descending" If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Name" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "C14", "E14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Type" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "F14", "E14", "C14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Size" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "E14", "C14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "Last Modified" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "G14", "C14", "E14") End If Case Default Exit Sub End Select End Sub
Ahora hemos escrito el código completo. Ahora podemos seleccionar la carpeta y el tipo de archivo deseados y encontrar la lista de archivos, que podemos ordenar por 'Nombre de archivo', 'Tipo de archivo', 'Tamaño de archivo' o 'Última modificación' y podemos exportar la lista a Excel o archivo de texto.

Cosas para recordar
Si el valor que especificamos para el argumento 'invertir' no está en la tabla de cadenas de entorno, la función ENVIRON devuelve la cadena de longitud cero.









